Quantification of dorsal column fiber responses in a model of kilohertz-frequency spinal cord stimulation
Abstract
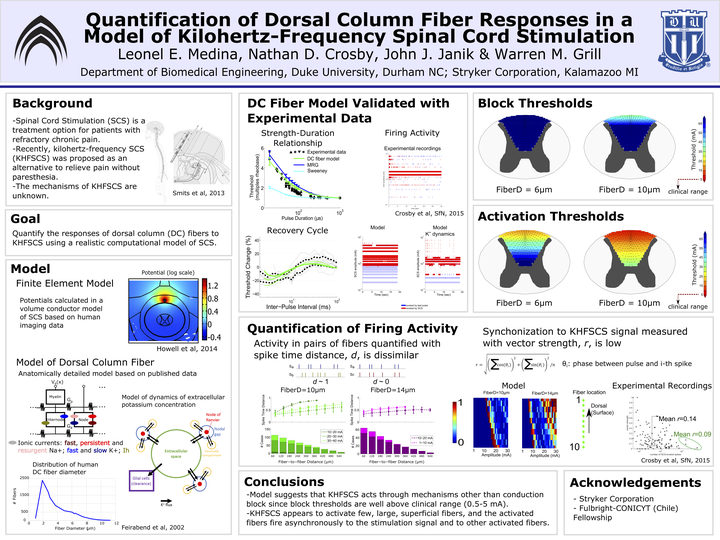
Introduction: Kilohertz-frequency spinal cord stimulation (KHF-SCS) was recently proposed as a paresthesia-free treatment for persons with chronic pain that is potentially more effective than conventional (~ 50 Hz) SCS. In SCS, the applied electrical stimulation is intended to activate the dorsal column (DC) axons. However, it is unclear how DC axons respond to kilohertz frequency signals. We developed a model of a DC fiber to quantify the responses of DC axons to the KHF-SCS signal.
Methods: We implemented a double cable model of a DC fiber using published morphological data and ion channel dynamics. We also recorded the strength-duration relationship and the recovery cycle of single DC axons in anesthetized rats for model validation. We coupled the axon model to a patient-specific volume conductor model of SCS and applied the KHF-SCS signal to quantify thresholds for activation and conduction block for different fiber diameters at different locations in the DCs. For cases exhibiting persistent activation, we quantified the degree of synchronization of the firing activity to the stimulation signal using the vector strength, and the similarity between the activities of pairs of fibers using the normalized spike time distance.
Results: Activation thresholds using the KHF-SCS signal increased sharply as the axons were placed deeper in the DCs. For the most superficial axons (< 500 um from the surface of the spinal cord), the activation thresholds for one patient averaged 57.2 ± 10.1 mA, 19.1 ± 6.1 mA and 8.3 ± 3.2 mA for fiber diameters of 2, 6 and 10 um, respectively. Conduction block thresholds in the same DC region averaged 164.8 ± 20.4 mA, 61.2 ± 10.1 mA and 34.7 ± 9.0 mA, for fiber diameters of 2, 6 and 10 um, respectively. The vector strength over the 10 – 50 mA amplitude range averaged 0.16 ± 0.09 and 0.11 ± 0.08 for 6 and 10 um diameter fibers, respectively, indicating a low degree of synchronization to the KHFSCS signal. For any given signal amplitude, the spike time distance decreased as the axons were placed at closer distances, but it was always greater than 0.5.
Conclusion: Our model results showed thresholds for activation and block of DC axons well above the amplitudes used clinically (1 – 5 mA). If the KHF-SCS signal activates large superficial axons, then the axons would fire asynchronously to the stimulation signal and to other axons.